Mercy Juma/BBC
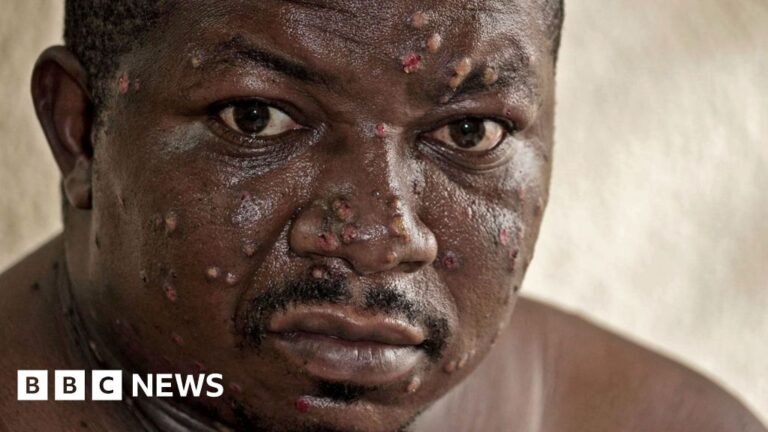
Mercy Juma/BBCEgide Irambona, 40, sat shirtless in a hospital mattress, close to a window in a therapy room he shared with two different males.
The night solar shone over Bujumbura, the principle metropolis of Burundi, and his face, bathed in delicate gentle, was coated in blisters. His chest too, and his arms.
“The lymph nodes in my throat had been swollen. It was so painful that I could not sleep. Then the ache there subsided and moved to my leg,” he advised the BBC.
Mr. Ilambona suffers from MPOX.
He’s one in every of greater than 170 confirmed circumstances recorded in Burundi since final month. It is among the world’s poorest nations and borders the Democratic Republic of Congo, the epicenter of a number of current MPO outbreaks which have killed at the very least 450 individuals and 14,000 suspected circumstances up to now this yr.
In Burundi, the place no deaths have been recorded, it’s unclear how lethal the present outbreak of a brand new pressure referred to as Clade 1b is as a result of there may be inadequate capability in affected areas to conduct testing.
Nonetheless, it has been declared a worldwide well being emergency attributable to considerations that it may unfold quickly to beforehand unaffected nations and areas.
That is Mr. Ilambona’s ninth day of therapy at King Khalid College Hospital. A technique the virus spreads is thru shut contact with an contaminated individual, who seems to have handed it on to his spouse.
She can also be being cared for on the similar facility.
“I had a pal who obtained blisters. I believe I obtained them from him. I did not realize it was MPOX. Fortunately, none of our seven youngsters confirmed any indicators of an infection,” mentioned Ilan Bona mentioned the gentleman, his voice trailing off.
The hospital in Bujumbura is residence to one in every of three MPOX therapy facilities within the metropolis.
Fifty-nine of the 61 accessible beds are occupied by contaminated sufferers, a 3rd of whom are beneath the age of 15, and based on the World Well being Group, youngsters are probably the most affected age group right here.
 Mercy Juma/BBC
Mercy Juma/BBCOdette Nsavyimana, the hospital’s chief doctor, mentioned the variety of sufferers was growing.
“We’re organising tents outdoors now.” To this point, there are three – one for triage, one for holding suspected circumstances, and one for receiving confirmed circumstances earlier than transferring them to wards.
“It is laborious, particularly when the infants are born. They cannot be left alone, so I’ve to depart their moms right here too. Even when they have no signs… it is a actually robust scenario,” Nsawima Dr. Na mentioned, her voice deepened by the sound.
Burundi is presently experiencing a surge in MPO circumstances.
“I am involved about these numbers. In the event that they proceed to extend, we cannot have the capability to cope with this.”
We make quite a lot of efforts to isolate contaminated individuals from the remainder of the hospital. Pink tape abounds, and guests are required to put on protecting gear and keep bodily distance from contaminated individuals.
 Mercy Juma/BBC
Mercy Juma/BBCMedical officers fear about restricted sources. The nation has just one laboratory that may check blood samples for the virus, a scarcity of check kits and no vaccine.
Sustaining sanitary circumstances all through Bujumbura can also be tough attributable to restricted primary sources corresponding to water within the metropolis. Working water was scarce and folks queued at public faucets.
Dr. Lilian Nkengulutes, nationwide director of the Public Well being Emergency Operations Heart, mentioned she is admittedly anxious concerning the coming days.
“It is a actual problem. The truth that analysis is simply completed in a single place delays the detection of recent circumstances.
“The well being heart referred to as the laboratory to say that they had a suspected case, however it took time for the laboratory staff to deploy to the place the suspected case was to gather samples.
“And it takes extra time to launch check outcomes. We’d like about $14 million (£10.7 million) to at the very least take our response to the subsequent stage,” she mentioned.
Whereas there are rumors that vaccines may arrive within the Democratic Republic of Congo as early as subsequent week, there have been no studies of comparable motion in Burundi.
 Mercy Juma/BBC
Mercy Juma/BBCThe general public’s consciousness of MPOX is proscribed.
Simply 20 minutes from the border with the Democratic Republic of Congo, Bujumbura is a hub for cross-border journey and commerce. However they had been unaware of the doable dangers of the epidemic.
Town is bursting with exercise. Individuals are nonetheless shopping for and promoting items as ordinary. Handshakes, hugs and really shut contact are the norm. Lengthy queues fashioned in entrance of bus stops as individuals rushed to board already packed public service automobiles.
“Many individuals do not perceive the seriousness of the issue. Even the place there are circumstances, persons are nonetheless simply socializing,” Dr. Nkenguluz mentioned.
The BBC spoke to some individuals in Bujumbura and most of them had no thought what MPOX was. And people who accomplish that do not understand it is spreading of their nation.
“I’ve heard about this illness however by no means seen anybody with it. I’ve solely seen it on social media,” one individual mentioned.
“I do know it impacts infants and younger individuals. I am scared, however that does not imply I will keep residence. I’ve to work. My household has to eat,” mentioned one other.
Well being employees know that persuading individuals to be extra cautious may be tough for a skeptical inhabitants dealing with a bunch of economic challenges.
However they are going to proceed to deal with sufferers, guarantee they recuperate, and attempt to hint those that have come into contact with them to curb the unfold of the virus.
Extra BBC tales about MPOX:
 Getty Pictures/BBC
Getty Pictures/BBC